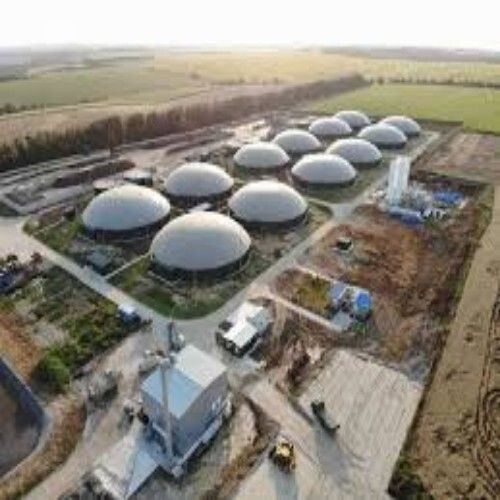
CBG Plant
Product Details:
- Product Type Industrial
- Application Other
- Hydrogen Content (%) 1%
- Methane Content (%) 96
- Nitrogen Content (%) 2
- Sulphur Content (%) 1
- Purity(%) 96
- Click to View more
CBG Plant Price And Quantity
- 1 Unit
- 100000000 INR/Unit
CBG Plant Product Specifications
- 96
- 96
- 1%
- 2
- Other
- Industrial
- 1
CBG Plant Trade Information
- Vadodara
- Cash Advance (CA) Cash in Advance (CID) Cheque
- 2 Unit Per Year
- 6 Months
- Asia Australia Central America North America South America Eastern Europe Western Europe Middle East Africa
- All India
Product Description
A Bio CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) plant is a facility that produces renewable CNG from organic waste materials. This process involves several key stages:
-
Feedstock Collection: Organic waste materials such as agricultural residues, food waste, or animal manure are collected. These materials are rich in organic matter and can be used to produce biogas.
-
Anaerobic Digestion: The collected organic waste is fed into an anaerobic digester, where microorganisms break down the organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This process produces biogas, which is primarily composed of methane (CH) and carbon dioxide (CO).
-
Biogas Upgrading: The raw biogas is processed to remove impurities and increase the methane content. This upgrading process typically involves removing CO, hydrogen sulfide (HS), and other contaminants to produce high-purity methane.
-
Compression: The purified methane is then compressed to form CNG. This involves compressing the methane gas to a high pressure, which makes it suitable for storage and use as a fuel.
-
Distribution and Utilization: The compressed natural gas can be stored in high-pressure cylinders or tanks and distributed for use as a fuel in vehicles, for power generation, or for other industrial applications.
Benefits of Bio CNG Plants:
- Sustainability: Bio CNG is a renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Waste Management: Helps in the effective management and reduction of organic waste.
- Reduced Emissions: Producing and using Bio CNG can lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels.
- Energy Security: Provides a local source of energy, enhancing energy security.
Bio CNG plants can vary in size from small-scale units designed for local use to large industrial facilities. The design and technology used will depend on the scale of the plant and the type of feedstock being used.


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS Call Me Free
Call Me Free